状态管理库pinia
状态管理库基本介绍
所谓状态管理库,就是用于管理一个应用中组件的状态的。
传统方式组件之间传递状态:
- 父传子用 Props
- 子传父用 Emit
这种方式存在的问题?
如果你的应用的规模一旦慢慢变大,那么不同层级之间组件的状态传递,就会变得非常的麻烦。
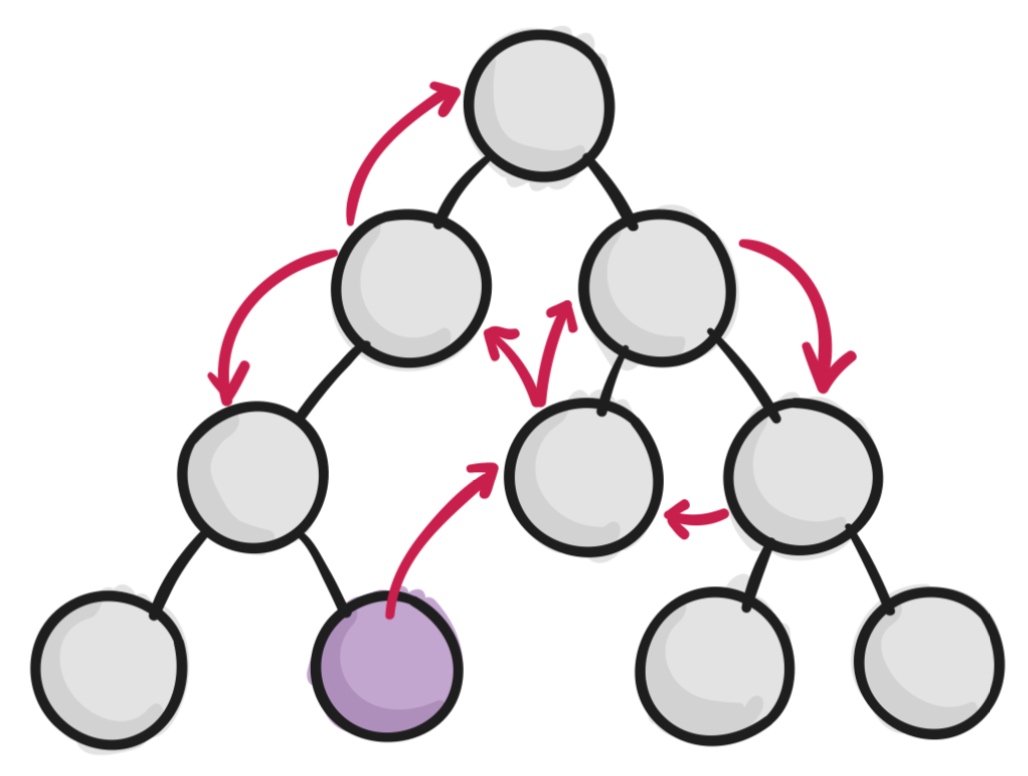
状态管理库如何解决这个问题的?
在状态管理库中,会有一个统一的地方(数据仓库)管理所有的状态,这个时候组件之间要进行状态的传递,只需要一个组件将状态提交到仓库,然后另一个组件从仓库获取最新的状态即可。
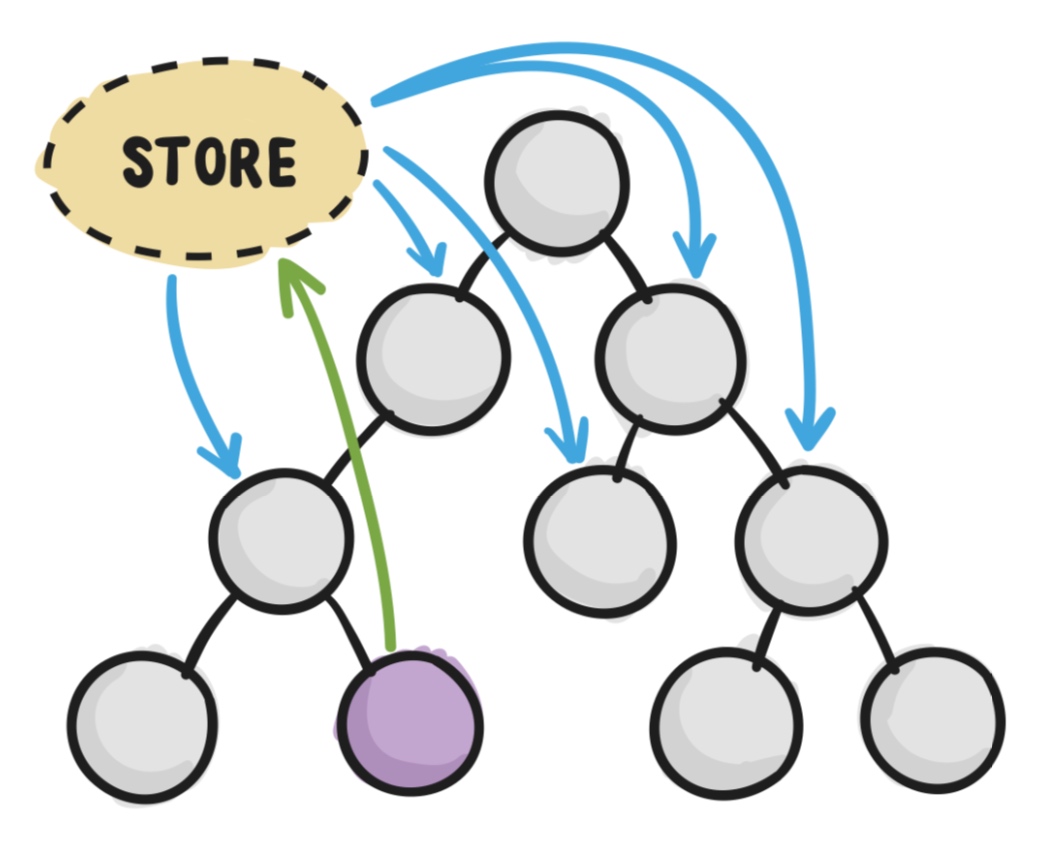
Vue生态的状态管理库
目前,Vue 生态官方所推荐的状态管理库是 Pinia,这是目前最新的状态管理库,用于替代以前的 Vuex 的,因此我们也是以 Pinia 为主,介绍这个最新的状态管理库。
Pinia ,发音为 /piːnjʌ/,来源于西班牙语 piña 。意思为菠萝,表示与菠萝一样,由很多小块组成。在 Pinia 中,每个 Store 都是单独存在,一同进行状态管理。
Pinia 是由 Vue.js 团队成员开发,最初是在 2019 年 11 月左右作为一项实验性工作提出的,目的是为了使用 Composition API 重新设计 Vuex,探索 Vuex 下一次迭代会是什么样子。但是 Pinia 在设计之初就倾向于同时支持 Vue 2 和 Vue 3,并且不强制要求开发者使用组合式 API。在探索的过程中,Pinia 实现了 Vuex5 提案的大部分内容,于是就直接取而代之了。
目前 Vue 官方已经宣布 Pinia 就是新一代的 Vuex,但是为了尊重作者本人,名字保持不变,仍然叫做 Pinia。
与之前的 Vuex 相比,Pinia 提供了更简单的 API,更少的规范,以及 Composition-API 风格的 API 。更重要的是,与 TypeScript 一起使用具有可靠的类型推断支持。
Pinia 官网地址:https://pinia.vuejs.org/
对比之前的 Vuex,Pinia 具有如下的特点:
- mutations 不复存在。只有 state 、getters 、actions
- actions 中支持同步和异步方法修改 state 状态
- 与 TypeScript 一起使用具有可靠的类型推断支持
- 不再有模块嵌套,只有 Store 的概念,Store 之间可以相互调用
- 支持插件扩展,可以非常方便实现本地存储等功能
- 更加轻量,压缩后体积只有 2kb 左右
1.快速入门
vuex是单独管理一个大的store,而pinia可以认为是每一个模块都是单独的状态,并且取消了复杂的mutations。
pinia的出现,相当于让人们并没感觉加什么插件,就好像自己写了一个hooks来进行使用。
npm i pinia --save //安装pinia
srtore -- index.js //创建文件夹和仓库文件main.ts
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './3-Vuex/App.vue'
import router from './3-Vuex/router'
import {createPinia} from 'pinia';//引入pinia
var app = createApp(App)
const pinia=createPinia();//实例化pinia
app.use(router);
app.use(pinia) //注册pinia插件
app.mount('#app')1.定义store
新建store文件夹--userStore.js中:
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
//1.命名:使用useXXX来命名,更符合我们的组合式API。
//2.defineStore("main",{//配置})
// --第一个参数:应用中 Store 的唯一 ID。
// --第二个参数:放状态管理的配置。
export const useStore = defineStore('main', {
// 其他配置...
})2.state
state 都是你的 store 的核心。人们通常会先定义能代表他们 APP 的 state。在 Pinia 中,state 被定义为一个返回初始状态的函数。这使得 Pinia 可以同时支持服务端和客户端。
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
export const useUserStore=defineStore("main",{
//state一般存放数据状态。
//在pinia里为了完整类型推理,推荐使用箭头函数,在return中写入自己存放的数据
state:()=>{
return {
// 所有这些属性都将自动推断出它们的类型
userName:"张三"
}
}
})2.1 组件中使用state的数据
在store中定义的状态和方法都会挂载到store对象下,不需要在store.state.xxx来进行访问,直接store.xxx访问即可。
//引入store
import useUserStore from "@/store/userStore"
//定义store
let store =useUserStore();
//使用状态数据
console.log(store.userName);**注意:**对store进行解构是会丢失相应式的,pinia提供了一个storeToRef()函数,来进行支持解构。
const {username} =storeToRef(useUserStore());2.2 组件中修改state的数据
1.直接修改store中的状态
2.使用store.$patch()修改。
3.使用actions定义的方法修改
//1.直接修改(单个修改)
store.userName="李四";
//2.批量修改
store.$patch({
userName:"二哥",
age:18,
})
//3.使用actions修改
store.changeUsername("李四");
//4.暴力修改
store.$state={
userName:"王五",
age:20
}2.3 一些方法
$reset()--重置仓库中的state数据,重置为初始状态
$patch()--批量修改数据,使用之后会自动的和state选项中的状态进行合并。3.Getters
getters相当于pinia的计算属性。
getters不仅可以进行单独的访问,也可以进行传参,原理就是使用高阶函数,函数作为返回值,然后调用的时候传参即可。
export const useStore = defineStore('main', {
state: () => ({
count: 1,
}),
//定义getters
getters: {
//1.推荐使用箭头函数,并且它将接收 state 作为第一个参数:
doubleCount: (state) => state.count * 2,
//2.getter传参
doubleCount(){
return (price)=>{
state.count * price
}
}
},
})3.1在模板中访问getters
<template>
//使用getters
<p>Double count is {{ store.doubleCount }}</p>
</template>
<script setup>
//声明解构store
const store = useStore();
//1.setup中访问getter
console.log(store.doubleCount);//2
//2.setup中访问getter中访问getter传参
console.log(store.doubleCount(3));//3
</script>3.2访问同仓库下其他getter
通过
this,你可以访问到其他任何 getter。
export const useStore = defineStore('main', {
state: () => ({
count: 0,
}),
getters: {
// 类型是自动推断出来的,因为我们没有使用 `this`
doubleCount: (state) => state.count * 2,
//定义第二个getters
//不能使用箭头函数,因为我们要使用this来访问doubleCount
doubleCountPlusOne() {
//使用doubleCount
return this.doubleCount + 1
},
},
})3.3访问其他 store 的 getter
想要使用另一个 store 的 getter 的话,那就直接在 getter 内使用就好:
//引入API
import { useOtherStore } from './other-store'
export const useStore = defineStore('main', {
state: () => ({
// ...
}),
getters: {
otherGetter(state) {
//使用其他store下的getters
const otherStore = useOtherStore()
return state.localData + otherStore.data
},
},
})4.Actions
Action 相当于组件中的 method。
在actions中,this可以直接访问到该仓库的实例
export const useStore = defineStore('main', {
state: () => ({
userName: "张三",
}),
//定义action
actions: {
changeUserName(){
console.log(this);//有store的实例
this.userName="二哥";
}
},
})4.1 在模板中中使用actions
export default defineComponent({
setup() {
//使用useMainStore();
const main = useMainStore()
// 作为 store 的一个方法调用该 action
main.changeUserName()
return {}
},
})4.2访问其他 store 的 action
//引入useAuthStore(其他store)
import { useAuthStore } from './auth-store'
export const useSettingsStore = defineStore('settings', {
state: () => ({
preferences: null,
// ...
}),
actions: {
async fetchUserPreferences() {
//声明其他store
const auth = useAuthStore();
//使用其他store下的actions
if (auth.isAuthenticated) {
this.preferences = await fetchPreferences()
} else {
throw new Error('User must be authenticated')
}
},
},
})5. setupStore风格
这种风格是官网更推荐的,虽然确实做到了无感开发,但是个人更喜欢选项式的写法。
setupStore风格仅是在定义的时候有所区别,在组件内使用没有区别。
ref()定义的就是state状态,computed就是getters,自己写的函数就是getters。
import { defineStore } from "pinia";
import axios from "axios";
import { ref, computed } from "vue";
/*
注意此种风格defineStore()的第二个参数是一个箭头函数,而不是配置项
*/
const useCinemaStore = defineStore("cinema", () => {
//定义的state
const cinemaList = ref([]);
//定义的actions
const getCinemaList = async () => {
var res = await axios({
url: "https://m.maizuo.com/gateway?cityId=110100&ticketFlag=1&k=5385023",
headers: {
'X-Client-Info': '{"a":"3000","ch":"1002","v":"5.2.1","e":"16784170161263416169725953","bc":"110100"}',
'X-Host': 'mall.film-ticket.cinema.list'
}
})
cinemaList.value = res.data.data.cinemas
}
//定义的getters
const filterCinemaList = computed(() =>
(type) => {
return cinemaList.value.filter(item => item.eTicketFlag === type)
}
)
//要return出去,就像自己写了一个hooks
return {
cinemaList,
getCinemaList,
filterCinemaList
}
})
export default useCinemaStore6. pinia的持久化
pinia的持久化需要使用插件,官网文档:https://prazdevs.github.io/pinia-plugin-persistedstate/zh/
npm i pinia-plugin-persistedstate将插件挂载在pinia实例
import { createPinia } from 'pinia'
import piniaPluginPersistedstate from 'pinia-plugin-persistedstate'
const pinia = createPinia()
pinia.use(piniaPluginPersistedstate)使用:
1.选项式pinia
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
export const useStore = defineStore('main', {
state: () => {
return {
someState: '你好 pinia',
}
},
persist: true,//开启持久化
})2.组合式pinia
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
export const useStore = defineStore('main', ()=>{
let count = ref(10);//定义状态
}
persist: true,//开启持久化
})3.配置项(常用)
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
export const useStore = defineStore('main', {
state: () => ({
someState: '你好 pinia',
save: {
me: 'saved',
notMe: 'not-saved',
},
saveMeToo: 'saved',
}),
persist: {
key: 'my-custom-key',//定义在localstorage中的key名称
storage: sessionStorage,//可以改变存储方式
paths: ['save.me', 'saveMeToo'],//指定持久化存储哪些状态
},
})